- Mon - Sunday 8:00 AM - 10:00PM
- Phone: +91 9063139473
 Epic International Hospital, Jubilee Hills
Epic International Hospital, Jubilee Hills
- Mon - Sunday 8:00 AM - 10:00PM
- Phone: +91 9063139473
 Epic International Hospital, Jubilee Hills
Epic International Hospital, Jubilee Hills
Service Details
Interventional cardiology (IC)
Angioplasty is a medical procedure used to unblock or widen narrowed blood vessels that provide blood flow to the heart. To treat peripheral artery disease (PAD) and its symptoms of pain, cramping, and ulcers in the extremities, a combination of techniques is used. First, a balloon is inflated within the narrowed or blocked artery to widen it and improve blood flow. Then, a stent—similar to a small mesh tube—is inserted to keep the vessel open and prevent re-narrowing. This procedure, known as peripheral angioplasty, has been proven essential in managing PAD and significantly enhancing patients’ mobility and quality of life by improving blood circulation. Additionally, it lowers the risk of severe complications associated with impaired peripheral circulation.
Coronary Angioplasty
Minimally invasive procedure used to open blocked coronary arteries and restore blood flow to the heart.

Coronary Stenting
Placement of a small mesh tube (stent) inside a coronary artery to keep it open after angioplasty.

Atherectomy
A procedure that removes plaque from a blood vessel using a rotating shaver or laser to improve blood flow.
Cardiac Catheterization
Diagnostic procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the heart to check for heart conditions.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
Minimally invasive procedure to replace a narrowed aortic valve that fails to open properly (aortic valve stenosis).

Balloon Valvuloplasty
Procedure to widen a heart valve that has narrowed, using a balloon-tipped catheter.
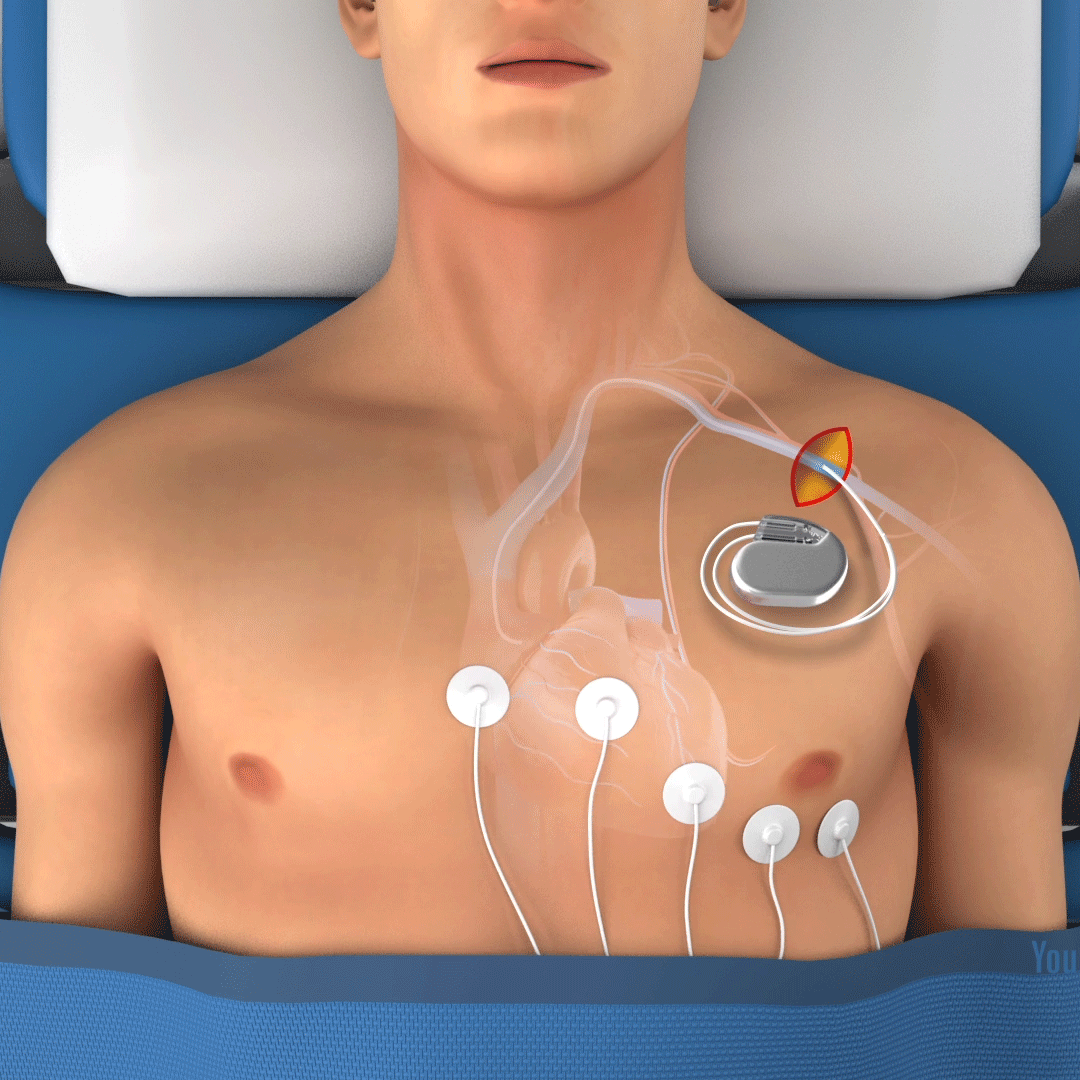
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs)
Device implanted in the chest to monitor heart rhythm and deliver shocks if dangerous arrhythmias occur.
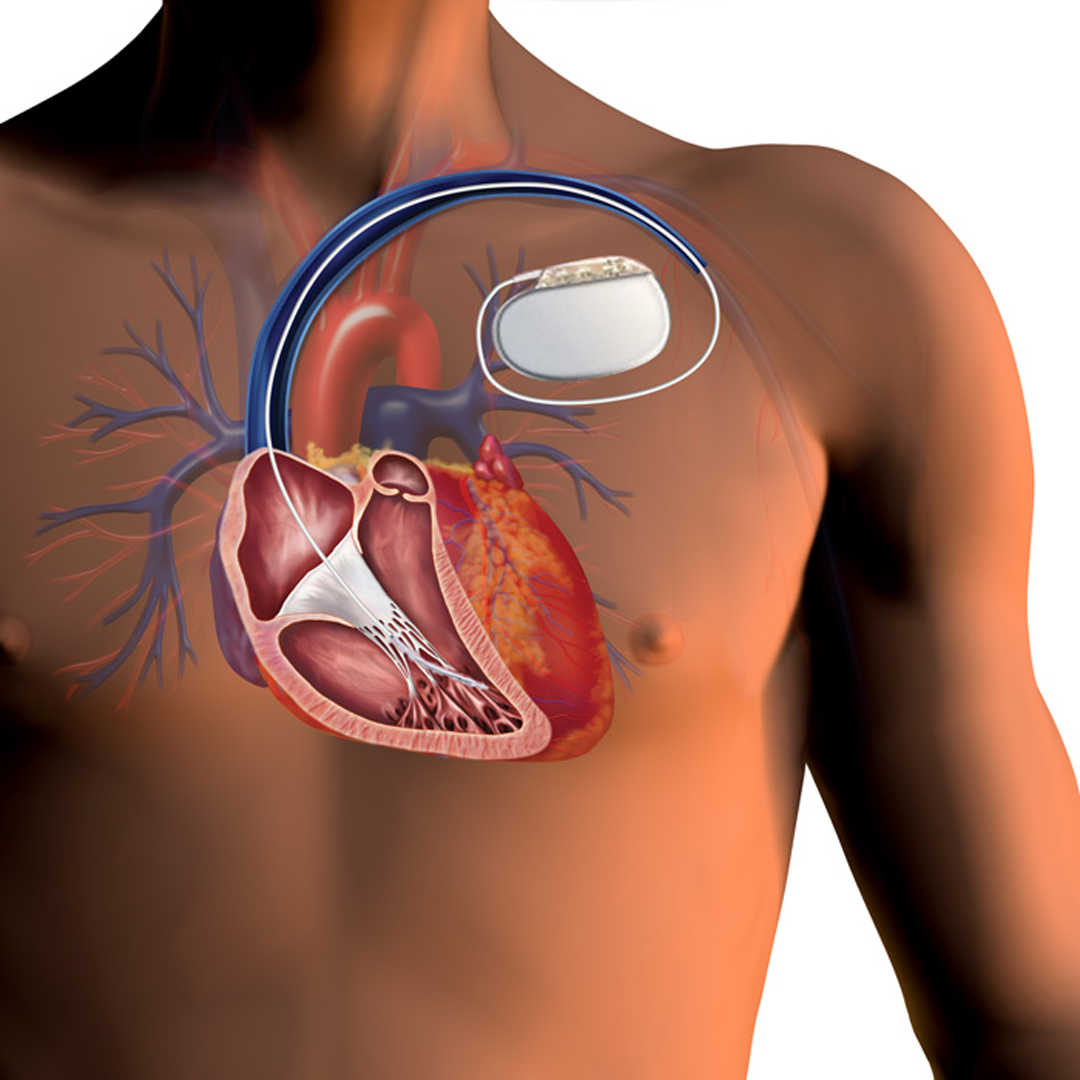
Pacemaker Implantation
A procedure to implant a small device that regulates slow or irregular heartbeats.
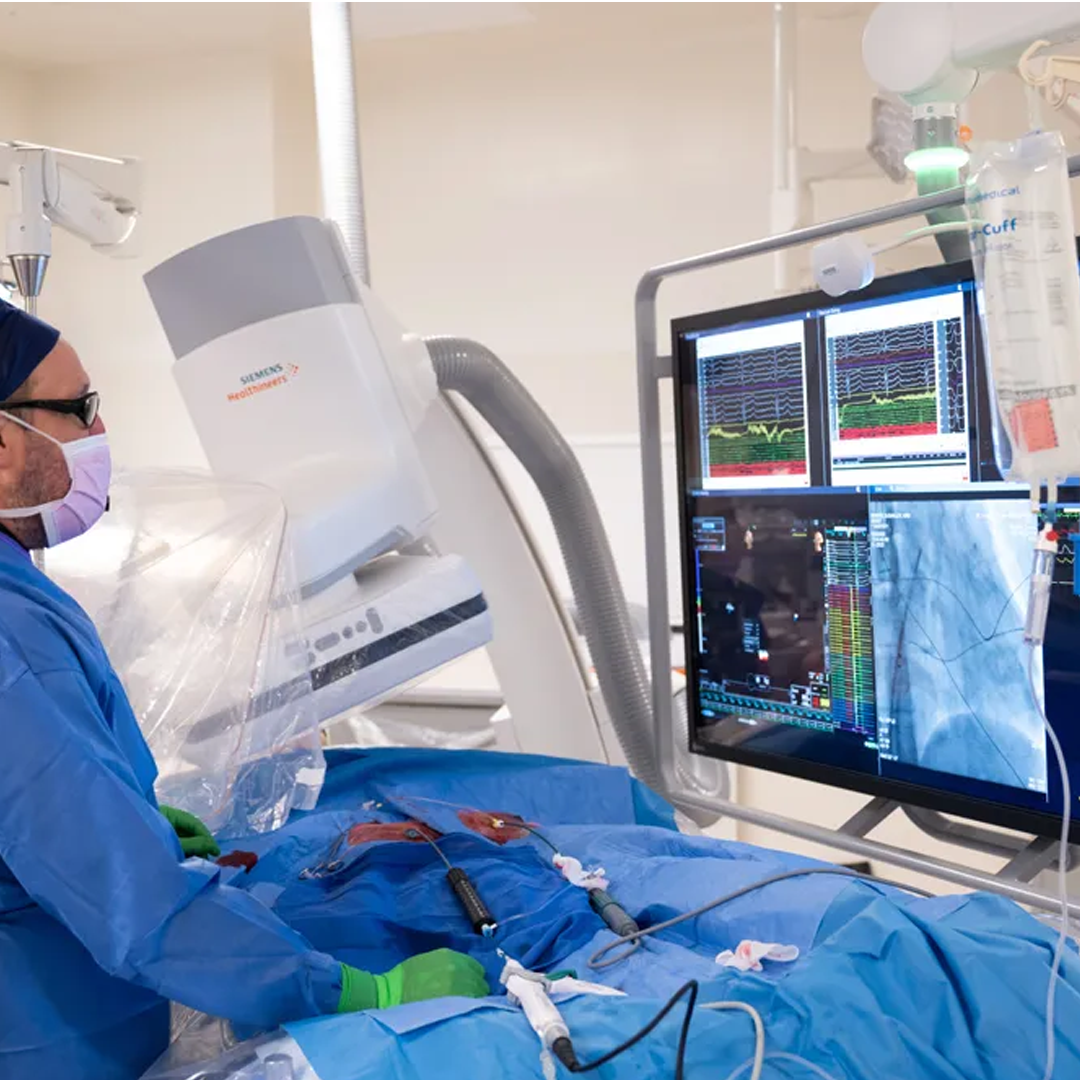
Electrophysiological Studies (EPS)
Tests to evaluate the electrical system of the heart and locate abnormal heart rhythms.

Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (LAAO)
Procedure to close the left atrial appendage and reduce stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation.